Kentucky hospitals gave $1.96 billion to communities in 2011, including $576.7 million cover of Medicare, Medicaid shortfalls
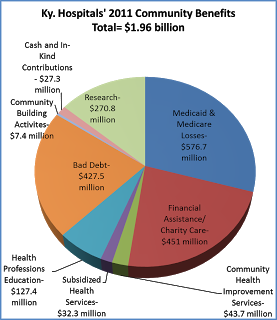
 In 2011, despite economic and financial obstacles, Kentucky hospitals’ estimated value of benefits to their communities up 17 percent from the year before, to $1.96 billion. So says the Kentucky Hospital Associated 2011 Community Benefits Report, compiled by the Kentucky Hospital Association with data submitted by hospitals. (Chart gives a breakdown of hospitals’ total community benefits and services expenditures in 2011.)
In 2011, despite economic and financial obstacles, Kentucky hospitals’ estimated value of benefits to their communities up 17 percent from the year before, to $1.96 billion. So says the Kentucky Hospital Associated 2011 Community Benefits Report, compiled by the Kentucky Hospital Association with data submitted by hospitals. (Chart gives a breakdown of hospitals’ total community benefits and services expenditures in 2011.)Kentucky hospitals say they absorbed $576.7 million in 2011 shortfalls from Medicaid and Medicare, which cover 19 and 55 percent of Kentucky hospital patients; those losses were 26 percent larger than 2010, and may nearly double under federal health reform, to an estimated $852 million by 2019.
Bridging gaps created by Medicaid and Medicare underpayment is only one example of how the 131 Kentucky hospitals demonstrate their commitment to local communities by investing in community needs, the report says. In addition to covering government shortfalls, community benefits include providing charity care, forgiving bad debt and supporting medical research.
 In Glasgow, T.J. Sampson Community Hospital and Dr. Bharat Mody (left), a general surgeon, have teamed up to fulfill the unmet health care needs of low-income, working, uninsured or under-insured adults of Barren County through a charity program called Community Medical Care. The program provides assistance with basic coverage for those who qualify, in addition to helping cover the cost of medications, glasses or hearing aids.
In Glasgow, T.J. Sampson Community Hospital and Dr. Bharat Mody (left), a general surgeon, have teamed up to fulfill the unmet health care needs of low-income, working, uninsured or under-insured adults of Barren County through a charity program called Community Medical Care. The program provides assistance with basic coverage for those who qualify, in addition to helping cover the cost of medications, glasses or hearing aids. In 2011, Kentucky hospitals absorbed $426.5 million in bad debts, losses due to patient non-payment that often occur in hospital emergency rooms. Dennis Manners, who had a $500,000 medical bill and sometimes visited the ER 25 times a month, is one patient out of the total 22 percent of University of Louisville patients who cannot afford care and often cannot even afford their $15 co-pay. Highlighting its efforts to give back to the community, the reports says U of L developed a new treatment plan for Manners, which included sending him to a treatment center outside of Cincinnati.
 Many health-improvement services in Kentucky communities, such as health fairs, screening programs, immunization clinics, health needs assessments and community planning, are financed by Kentucky hospitals. According to the report, $43.7 million was spent by these hospitals on such outreach programs that serve all ages and a number of special needs populations. For example, Northern Kentucky’s St. Elizabeth Healthcare is fighting against cardiovascular disease, diabetes and stroke with its Cardiovascular Mobile Health Unit that brings vascular services to the community for easy access, screenings, risk appraisals and education.
Many health-improvement services in Kentucky communities, such as health fairs, screening programs, immunization clinics, health needs assessments and community planning, are financed by Kentucky hospitals. According to the report, $43.7 million was spent by these hospitals on such outreach programs that serve all ages and a number of special needs populations. For example, Northern Kentucky’s St. Elizabeth Healthcare is fighting against cardiovascular disease, diabetes and stroke with its Cardiovascular Mobile Health Unit that brings vascular services to the community for easy access, screenings, risk appraisals and education.  Other community benefits include subsidized health services, estimated at $32.3 million, to support programs like Highlands Regional Medical Center‘s Highlands Center for Autism in Prestonsburg (left). The center is the first of its type in the state and was created in 2009 to address autism in Kentucky, which is estimated by the Center for Disease Control to be diagnosed in one out of every 88 children, says the report. Each child at the Highlands center has a customized treatments plan involving psychologists, educators, behavior analysts, speech pathologists, pediatricians and neurologists, who collaborate to help children with autism reach their full potential.
Other community benefits include subsidized health services, estimated at $32.3 million, to support programs like Highlands Regional Medical Center‘s Highlands Center for Autism in Prestonsburg (left). The center is the first of its type in the state and was created in 2009 to address autism in Kentucky, which is estimated by the Center for Disease Control to be diagnosed in one out of every 88 children, says the report. Each child at the Highlands center has a customized treatments plan involving psychologists, educators, behavior analysts, speech pathologists, pediatricians and neurologists, who collaborate to help children with autism reach their full potential. The annual KHA report reminds people what hospitals do for the state and provides education about ongoing efforts. A more recognizable contribution is that Kentucky hospitals had a combined spending of $6.4 billion in 2011 on staff salaries, purchases or supplies and services that create a‘ripple effect” in the overall economy to generate state businesses, jobs, and tax revenue. The reports says St. Joseph Mount Sterling, for example, provided 213 jobs and generated about $12 million in annual local payroll in 2011. Kentucky hospitals’ compensation comprises 5.8 percent of all wages and salaries in the state.
The reports says hospitals are more important than ever to the overall economic health of Kentucky communities. This is the fourth year for the report, generated by the voluntary KHA survey and other data sources, including the annual survey by the American Hospital Association; Kentucky Hospital Statistics, 2013; and Kentucky Hospitals’ Economic Importance to Their Communities, 2011. The KHA report covers community benefit expenditures made in 2011, which is the most recent year for which statewide data is available.