State Supreme Court says county boards of health cannot enact smoking bans by regulation
Kentucky Health News
County health boards in Kentucky do not have the power to ban smoking in public places, the Kentucky Supreme Court ruled without dissent Thursday.
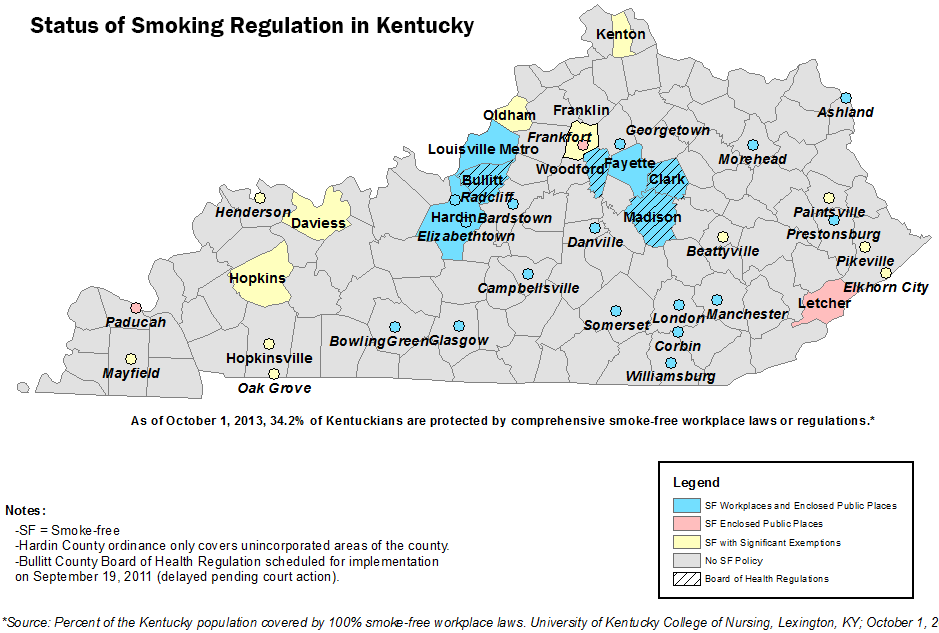
The decision was a stiff blow to health officials who see smoking as the primary factor in making Kentucky one of the least healthy states, and have sought state and local smoking bans to limit exposure to second-hand smoke. It struck down a ban in Bullitt County and presumably will do likewise for those enacted by the Clark, Madison and Woodford county health boards, which joined the case. (Click on map for larger version)
Justice Bill Cunningham, who wrote the decision, noted that the U.S. surgeon general has found “many of the chemicals inhaled through second-hand smoke are known carcinogens” and “that even short-term exposure to second-hand smoke can result in serious health consequences. In 2009-10, overall second-hand smoke exposure by Kentucky adults was 51.4 percent, with 30 percent reporting exposure in the workplace and 32.8 percent reporting exposure in public places. Given such dismal data, it is understandable that many health-care professionals and government officials have sought to curtail the prevalence of this noxious fume. Promoting a smoke-free society is a reasonable goal grounded in sound research. However, when promotion becomes enactment, even the most virtuous causes must also be grounded in law.”
Health boards enacting bans have relied on a 1954 state law that gives them to power to adopt regulations “necessary to protect the health of the people.” To find that law as “sufficient grounding for the regulation,” Cunningham wrote, the court would have to construe the law “as delegating the totality of the Commonwealth’s police power to the health boards. Nothing would remain to be ceded by the General Assembly, including the critical legislative charge of distinguishing virtue from vice.”
Cunningham said such a ruling would “promote an overly broad delegation of legislative sovereignty,” in violation of the state constitution. He said the authorization of regulations was limited, and was based that view on what he called the law’s legislative history. In 1954, he wrote, “It would have been
commonplace for members of the General Assembly to indulge in a cigarette or cigar in their offices, committee rooms, or even on the floors of the House and Senate chambers. Most likely, the . . . legislation was debated and voted in chambers fogged with a haze of smoke.”
Thursday’s decision overturned a 2-1 ruling of a Court of Appeals panel that relied partly on the 1984 Supreme Court decision that upheld a Jefferson County regulation on lead paint. Cunningham said that was based on a law that “specifically addressed lead poisoning and expressly authorized and encouraged action at the local level,” and “There is no similar statutory mandate” in state law for smoking bans.
Cunningham also noted that most of the Jefferson County board is appointed by local officials, while health boards in other counties are appointed by the state health secretary “and not by duly elected representatives. When regulating controversial issues traditionally within the province of state or local legislative entities, this structure is constitutionally problematic in that it does not comport with traditional notions of representative government.” In this case, the Bullitt County Fiscal Court filed a lawsuit challenging the health board’s authority.
The appeals court, in rejecting the fiscal court’s case and overturning the local circuit court, also relied on a 1967 decision upholding a local health board’s regulation of private sewage disposal systems. Cunningham said that decision was strongly based on earlier cases on the topic, and in contrast, there is no “well-established line of authority regarding the need for administrative regulation of smoking and second-hand smoke.”
Finally, Cunningham said legal precedents in Kentucky say that “Where reasonable doubt exists concerning the proper scope of an administrative agency’s authority, it should be resolved against the agency,” and “An increase in the aggregate power of administrative agencies over the recent decades, if left unchecked, invites the ascendance of a fourth branch of government—the regulatory state.”
